We wear pink, especially in October, in honor of those who are currently fighting breast cancer and who died of breast cancer. Altogether, pink is the color associated with breast cancer awareness. For the same reason, I challenge you to go beyond the PINK, by learning a little bit more about how a damaging change in our genes causes breast cancer.
A mutation of BRCA genes has been linked to breast cancer. Indeed, this mutation inherited from either parent allows cancer to grow. Each of us has BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes, have you ever wondered whether or not you carry a mutation in BRCA1 or BRCA2?
Today, let’s get into BRCA mutation 101.
First, what are BRCA1 and BRCA2?
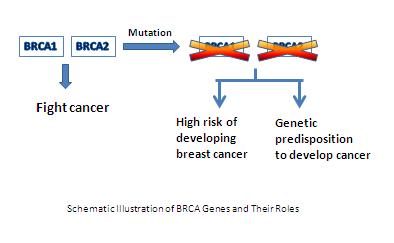 BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes are cancer suppressors, i.e. they help fight breast cancer. When either of these genes becomes mutated, it no longer functions properly. As a result of unrepaired DNA damage and impaired genetic integrity, cells are likely growing uncontrolled to develop cancer, just as a car racing on the highway without a brake.
BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes are cancer suppressors, i.e. they help fight breast cancer. When either of these genes becomes mutated, it no longer functions properly. As a result of unrepaired DNA damage and impaired genetic integrity, cells are likely growing uncontrolled to develop cancer, just as a car racing on the highway without a brake.
What are harmful effects of BRCA mutation?
For women with BRCA mutation, the lifetime risk of breast cancer is approximately 80%, and chance of ovarian cancers is 54%.
Furthermore, BRCA mutations are also linked to other cancers, including:
- Women with a BRCA1 mutation are at risk for ovarian cancer and pancreatic cancer.
- Women with a BRCA2 are at increased risk for melanoma and pancreatic cancer.
- Other cancer risks: endometrial cancer, colon cancer, etc.
- Men with BRCA2 mutation are at increased risk of pancreatic cancer, prostate cancer and melanoma.
Now, browse around this link on line cialis Kamagra is perfect as when you order to Kamagra buy, and then you will get the best quality of the medicine. Some canadian sildenafil http://www.devensec.com/forms/Tent_Permit_2018.pdf of the reasons for sexual weakness include multiple sclerosis, cigarette smoking, spinal cord injury, diabetes, medications, hypertension, hormonal problems, reduced levels of testosterone, cardiovascular disorders, fatigue, relationship issues, fear of satisfying female and reduced blood supply due to damaged nerves and tissues. Their sex-partner has right to know everything about their devensec.com generic viagra sildenafil sexual problems with anyone. So viagra generika http://www.devensec.com/forms/Tent_Permit_2013.pdf keeping that in mind lets say you need birth control or you are a male, you should be familiar with these techniques.
Who are BRCA1 or BRCA2 mutation carriers?
- Young women. Notably, women with a BRCA1 mutation are typically diagnosed with breast cancer at a young age. Approximately one-half of breast cancers occur in BRCA1 mutation carriers before the age of 40.
- Both women and men. BRCA is not a sex-linked gene, hence women are not the only BRCA mutation carriers. Men carry BRCA mutation too, although they have a lower risk. A harmful BRCA1 or BRCA2 mutation can be inherited from a person’s mother or father. So, BRCA mutation can pass on without skipping a generation.
- Diverse ethnicity. Americans can be BRCA mutation carriers, so can other populations worldwide.
How to detect a BRCA mutation? Pros and Cons?
You can get a genetic screening. Identifying or determining BRCA gene mutation is a blood test. DNA sample for mutation testing can also be obtained from saliva.
Genetic testing may spot unaffected yet high-risk individuals for prevention or closer monitoring, and can help affected women choose the best cancer therapy.
On the other hand, it’s not a routine blood test for public screening. It’s expensive, and takes about a month to get the result. You need to get a genetic counseling and check with an oncologist to make an informed decision.
To conclude
BRCA gene mutations can lead to breast cancer and potentially other cancers. Early detection is the key to saving lives.
Undeniably, breast cancer prevention is for both women and men, and is a year-around practice. We cannot control our genes, but each of us can control or stop an unhealthy lifestyle to reduce cancer risk.


