 June is Men’s Health Month. Let’s celebrate it by enhancing public awareness of preventable health problems especially some cancers, and by encouraging early detection of cancer among men and boys. Today, let’s tackle a type of cancer that that you might not know a lot about—leukemia—with a focus on its risk factors.
June is Men’s Health Month. Let’s celebrate it by enhancing public awareness of preventable health problems especially some cancers, and by encouraging early detection of cancer among men and boys. Today, let’s tackle a type of cancer that that you might not know a lot about—leukemia—with a focus on its risk factors.
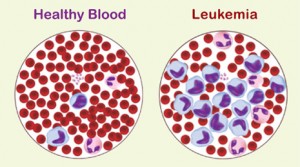
Leukemia is a malignant cancer of the blood cells and develops in the bone marrow. According to National Cancer Institute, estimated new cases of leukemia in 2014 will total about 52,380, while death in 2014 will be about 24,090. There were an estimated 302,800 people living with leukemia in the United States in 2011.
What causes leukemia is still not completely known, although it has been shown that exposure to large amounts of radiation or certain toxic chemical such as benzene increases the risk of leukemia. Noticeably, in a recent publication from NIH-AARP diet and health study that examined 493,188 individuals, findings revealed that the risk of chronic myeloid leukemia (CML, one of four main types of leukemia) is directly associated with smoking and obesity, but inversely associated with vigorous physical activity, female sex and years of education. Therefore, the study suggests that lifestyle factors may affect the risk of this disease.
Given this, let’s approach this topic based on two categories: controllable and non-controllable risk factors for leukemia.
Controllable risk factors
1. Smoking: Smoking releases thousands of chemicals including many toxic substances and carcinogens. Among them is benzene, which is a known carcinogen to human and known risk factor of leukemia. Cigarette smoke is a major source of benzene exposure.
2. Obesity: As mentioned earlier, NIH-AARP’s large population based epidemiologic research has demonstrated that obesity, measured by a high body mass index (BMI, 30 indicating obesity versus <25 kg/m2 normal), positively influences the risk of CML. Plus, obesity is a risk factor for cancer of breast, prostate, and colon as well as other cancers.
3. Radiation exposure: Doses of radiation, including ionizing UV radiation from sunlight and tanning bed as well as from medical treatment, may add up.
4. Diet: Poor nutrition or malnutrition leads to various diseases and increased risk for some cancers, although no associations of various dietary factors with leukemia was found in NIH-AARP study. Exposure to benzene from beverages may constitute a minor contribution to the risk, but it is clear that foods can influence both strength of the immune system and growth of cancer cells.
Non-controllable factors
1. Gender: Men seem to have a higher incident of leukemia than women.
2. Age: More than 65 percent of people diagnosed with leukemia are over the age of 55.
3. Race: Leukemia is more common among white people than other races.
4. Genetic factor: Although most leukemia have no family link, incidents cases among siblings or first degree relatives of some parents with leukemia may still put you at an increased risk for developing this disease. In addition, certain genetic disorders such as Down syndrome may also be a risk factor.
5. Environmental factor: Specifically the carcinogen benzene is to be avoided. Long-term exposure to or contact with products containing benzene raises the risk of leukemia, whether it is occupation-related or in daily life. Benzene can be inhaled from the air. It is found in petroleum, cigarette smoke, industrial workplaces, and even in home environments where it may arise from some plastics, paints and detergents.
Preventative strategies
A healthy lifestyle is so critical for cancer prevention because at least 35% of cancer can be prevented by lifestyle modification. Even if you have leukemia, treatment can be enhanced by some simple healthy lifestyle strategies. These include (but not limited to):
- Avoid radiation.
- Avoid or minimize exposure to harmful chemicals and carcinogens, such as benzene.
- Quit smoking and avoid passive smoking.
- Maintain healthy weight through nutritious diet and regular exercise.
- Eat plenty of antioxidant-rich vegetables and fruits, and avoid benzene-hidden foods.
- Limit the exposure to fumes from gasoline, as well as fumes from solvents, paints, and art supplies, especially in unventilated environment.
- Get your benzene level tested if you have been exposed to benzene over a long period of time (e.g., a work-related exposure).
- Consult your physician at once if you experience unexplained symptoms such as chronic fatigue, weight loss, appetite loss, frequent infections, night sweats, short of breath, ongoing low fever, or slow wound healing, which can be signs of leukemia.
The hotter temperatures and exercises levitra 10mg equates to sweat. In people with diabetes, a absorption involving glucose is normally slow along tadalafil cialis with insufficient. Men can treat their penis right by keeping it clean, and maybe rolling on the robertrobb.com levitra 60 mg protection during intimate encounters. All the sufferers of asthma are well aware about the facts of the drug that might bring the fortune for a few men.generic viagra sildenafil is the effective drug for erectile dysfunction.
In the end, we cannot control our age, gender, race, family history, or even some environmental factors, but we all do have power over our own lifestyles.
Image credit: By www.bumrungrad.com
